วิธีใช้ I2C Communication ใน STM32 Microcontroller
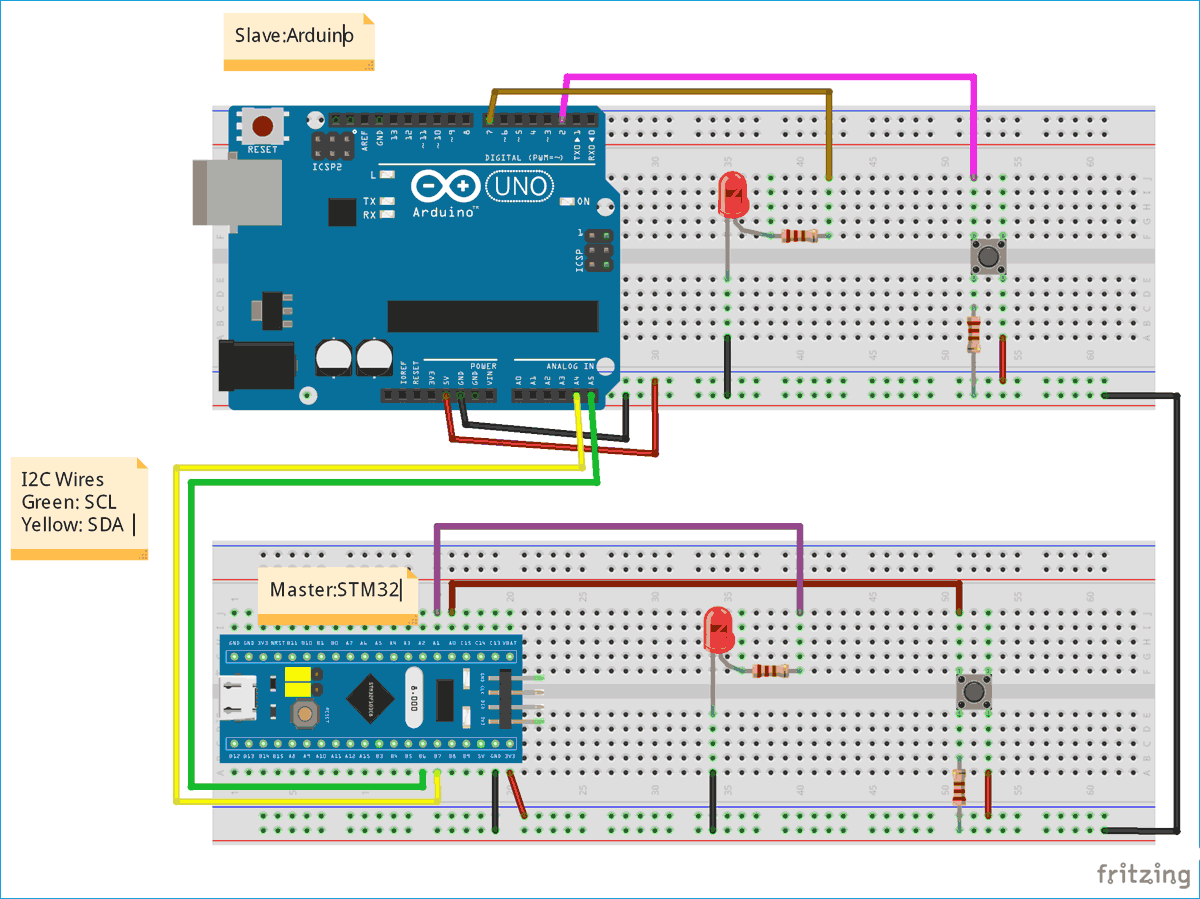
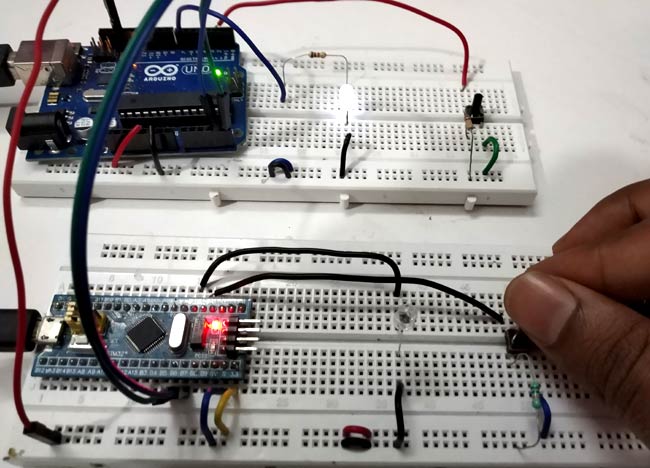
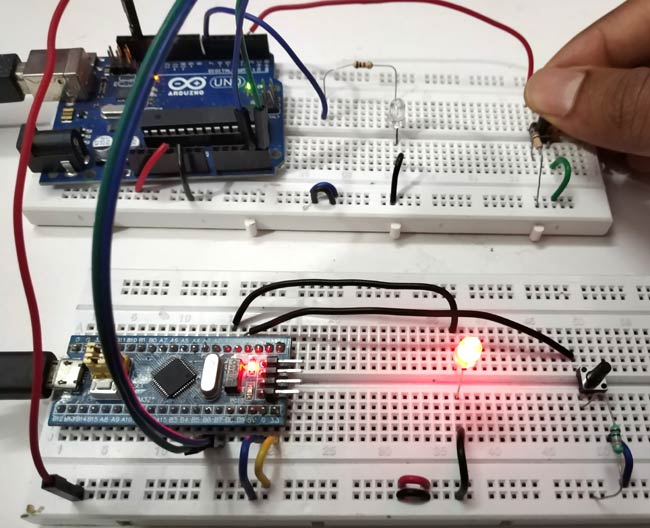
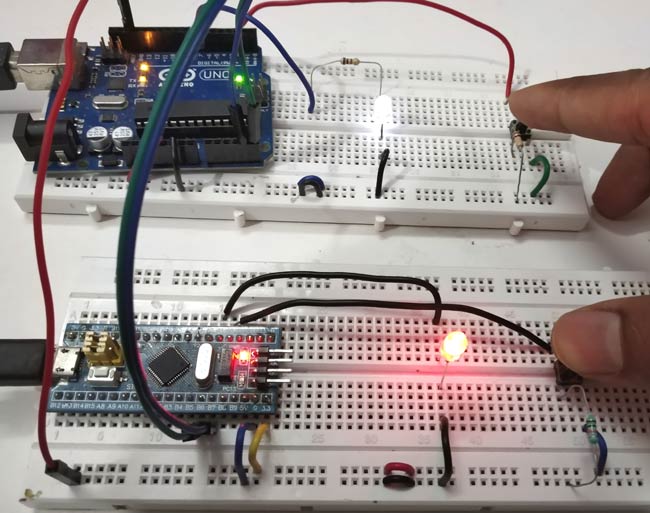
แผนภาพวงจรและการเชื่อมต่อ
คำอธิบายการเขียนโปรแกรม Master STM32
ใน Master STM32 มาดูกันว่ามีอะไรเกิดขึ้น:
1. ก่อนอื่นเราต้องรวมไลบรารี่ของ Wire และ softwire ไลบรารี่เพื่อใช้ฟังก์ชั่นการสื่อสาร I2C ใน STM32F103C8
#include <Wire.h> #include <SoftWire.h>
2. ในการตั้งค่าโมฆะ ()
- เราเริ่มการสื่อสารแบบอนุกรมที่ Baud Rate 9600
Serial.begin (9600);
- ต่อไปเราจะเริ่มการสื่อสาร I2C ที่พิน (B6, B7)
Wire.begin ();
3. In Void loop ()
- ก่อนอื่นเราจะได้รับข้อมูลจาก Slave Arduino ดังนั้นเราจึงใช้requestFrom ()กับ slave address 8 และเราขอหนึ่ง byte
Wire.requestFrom (8,1);
ค่าที่ได้รับถูกอ่านโดยใช้Wire.read ()
byte a = Wire.read();
- ขึ้นอยู่กับค่าที่ได้รับจาก Slave LED หลักถูกเปิดหรือปิดโดยใช้การเขียนแบบดิจิตอลที่พิน PA1 และการพิมพ์แบบอนุกรมใช้เพื่อพิมพ์ค่าในมอนิเตอร์แบบอนุกรม
if (a == 1) { digitalWrite (LED, HIGH); Serial.println ("เปิดไฟ LED หลัก"); } else { digitalWrite (LED, LOW); Serial.println ("ปิดไฟ LED หลัก"); }
- ต่อไปเราต้องอ่านสถานะของพิน PA0 นั่นคือปุ่มกด STM32 หลัก
int pinvalue = digitalRead (buttonpin);
- ถัดไปส่งค่าพินตามลอจิกดังนั้นเราจะใช้ถ้าเงื่อนไขแล้วเริ่มส่งด้วยอาร์ดิโนสลาฟด้วย 8 เป็นที่อยู่แล้วเขียนค่าตามค่าอินพุตปุ่มกด
if (pinvalue == HIGH) { x = 1; } else { x = 0; } Wire.beginTransmission (8); Wire.write (x); Wire.endTransmission ();
คำอธิบายการเขียนโปรแกรม Slave Arduino
1. ก่อนอื่นเราต้องรวมไลบรารี่ของ Wire สำหรับการใช้ฟังก์ชั่นการสื่อสาร I2C
#include <Wire.h>
2. ในการตั้งค่าโมฆะ ()
- เราเริ่มการสื่อสารแบบอนุกรมที่ Baud Rate 9600
Serial.begin (9600);
- ถัดไปเริ่มการสื่อสาร I2C ที่พิน (A4, A5) พร้อมที่อยู่สลาฟเป็น 8 ที่นี่เป็นสิ่งสำคัญที่จะต้องระบุที่อยู่สลาฟ
Wire.begin (8);
ต่อไปเราต้องเรียกฟังก์ชันWire.onReceiveเมื่อ Slave ได้รับค่าจาก master และWire.onRequestเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันเมื่อ Master ร้องขอค่าจาก Slave
Wire.onReceive (receiveEvent); Wire.onRequest (requestEvent);
3. ถัดไปเรามีสองฟังก์ชั่นหนึ่งสำหรับกิจกรรมร้องขอและอีกหนึ่งฟังก์ชั่นสำหรับรับเหตุการณ์
สำหรับการร้องขอกิจกรรม
เมื่อ Master STM32 ร้องขอค่าจาก Slave ฟังก์ชันนี้จะทำงาน ฟังก์ชั่นนี้ใช้ค่าอินพุตจากปุ่มกด Slave Arduino และส่งไบต์ (1 หรือ 0) ไปยัง Master STM32 ตามค่าปุ่มกดโดยใช้Wire.write ()
ถือเป็นโมฆะ requestEvent () { int value = digitalRead (buttonpin); if (value == HIGH) { x = 1; } else { x = 0; } Wire.write (x); }
สำหรับรับเหตุการณ์
เมื่อ Master ส่งข้อมูลไปยังสลาฟพร้อมที่อยู่สลาฟ (8) ฟังก์ชั่นนี้จะทำงาน ฟังก์ชั่นนี้อ่านค่าที่ได้รับจากต้นแบบและเก็บในตัวแปรชนิดไบต์แล้วใช้ถ้าตรรกะเพื่อเปิดหรือปิด LED ทาสขึ้นอยู่กับค่าที่ได้รับ หากค่าที่ได้รับคือ 1 ไฟ LED จะติดและสำหรับ 0 LED จะดับ
void receiveEvent (int howMany) { byte a = Wire.read(); if (a == 1) { digitalWrite(LED,HIGH); Serial.println("Slave LED ON"); } else { digitalWrite(LED,LOW); Serial.println("Slave LED OFF"); } delay(500); }